Research projects
Pilot real-time data collection of probable suicide deaths
 We are establishing a real-time data collection of suspected suicide deaths by people under the recent care of mental health services in England – specifically, in-patients and post-discharge patients who died within 14 days of discharge. This real-time surveillance (RTS) system will focus on patients closest to care and ask for information that we need to know early to support suicide prevention efforts. This includes emerging novel methods, suicide related internet use, possible clusters, problems in care which may be systemic and particular problems that patients face.
We are establishing a real-time data collection of suspected suicide deaths by people under the recent care of mental health services in England – specifically, in-patients and post-discharge patients who died within 14 days of discharge. This real-time surveillance (RTS) system will focus on patients closest to care and ask for information that we need to know early to support suicide prevention efforts. This includes emerging novel methods, suicide related internet use, possible clusters, problems in care which may be systemic and particular problems that patients face.
On 1st August 2023, we will begin piloting this real-time data collection in eight NHS Trusts in South East England only (see list below). We will be asking clinicians from these pilot trusts to complete an online questionnaire when they become aware of a suspected suicide by a patient under the care of their trust, without waiting for the inquest or for a request from us. This data collection will be extended nationally in 2024 (estimated) following feedback and learning from our pilot.
If you are a clinician working in one of our eight pilot trusts, please follow this link to further information and the online questionnaire. Frequently asked questions can be found here and our infographic for onward sharing is available here.
- Berkshire Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust
- Isle of Wight NHS Trust
- Kent and Medway NHS and Social Care Partnership Trust
- Oxford Health NHS Foundation Trust
- Solent NHS Trust
- Southern Health NHS Foundation Trust
- Surrey and Borders NHS Foundation Trust
- Sussex Partnership NHS Foundation Trust
Suicide in NHS staff: a national data collection to inform prevention
 We have been commissioned by NHS England to establish a prospective data collection about suicide by NHS staff, with the aim of preventing future deaths.
We have been commissioned by NHS England to establish a prospective data collection about suicide by NHS staff, with the aim of preventing future deaths.
Some health service staff may be at an increased risk of suicide, and staff wellbeing is a priority in the context of sustained and growing pressures.
We are taking a stepped approach to establishing this data collection:
- firstly, we are working with Greater Manchester NHS Integrated Care Board to engage with stakeholders and HR representatives across Greater Manchester as our trailblazer site to explore data availability for clinical staff;
- we will expand our engagement to the North-West region, to pilot retrospective data collection on all suicide deaths by NHS healthcare staff over a 5-year period;
- we will expand this data collection nationally, and further develop the data collection to collect information about non-clinical members of NHS staff who die by suicide. By learning from these tragic deaths, our aim is to improve safety and wellbeing for people working within the NHS. This work will run from May 2023 to April 2026.
National review of higher education student suicides
 We have been funded by the Department for Education to conduct an independent national review of suspected suicides (and non-fatal incidents of serious self-harm) in higher education (HE) students in England. This will enable broader lessons around mental ill-health and suicide in HE students, with the aim of preventing future deaths.
We have been funded by the Department for Education to conduct an independent national review of suspected suicides (and non-fatal incidents of serious self-harm) in higher education (HE) students in England. This will enable broader lessons around mental ill-health and suicide in HE students, with the aim of preventing future deaths.
We will undertake this by examining serious incident (SI) reviews of suspected suicide by HE students, conducted by HE providers in line with guidance published by Universities UK. The focus of the study is reviews conducted during the 2023/24 academic year but we will also consider some earlier reviews.
We are acutely aware of the sensitivity of this study and the interest in it from families bereaved by suicide. We have always worked closely with families and will be asking for their input throughout.
Specifically, we will:
- assess the quality of the SI reviews;
- identify the common themes in suspected suicide deaths in HE students;
- identify examples of good practice within the HE sector and areas needing improvement;
- the quality, validity and effectiveness of the guidance published by Universities UK will also be assessed.
Further information about the study can be found in our information sheet and FAQs. The study will report around spring 2025.
Reducing suicides: Quality improvement and patient safety
We are working with experts in Quality Improvement at the National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health (NCCMH) to support Sustainability and Transformation Partnerships (STPs) to strengthen their local suicide prevention quality improvement plans. This is part of a nationally recognised suicide reduction priority across Department of Health, NHS England, and an overall Mental Health Five Year Forward View recommendation to reduce the suicide rate by 10% by 2020/21.
Together with NCCMH, we are working with Quality Improvement teams in each STP to:
- review their services against established guidelines and recommendations, and improve the quality of care they offer, using bespoke data provided from the NCISH database, benchmarked against the national average;
- provide expert knowledge of suicide prevention in three priority areas – mental health secondary care, services for self-harm, and middle-aged men;
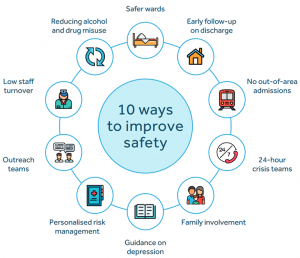
- identify and help STPs adopt and embed national evidence including NCISH “10 ways to improve patient safety” into local quality improvement plans;
- advise on local data collection and suicide prevention plans.
Read more about this collaboration on NCCMH’s Suicide Prevention National Transformation Programme webpage. The study is commissioned by the Healthcare Quality Improvement Partnership (HQIP).
In May 2019, NCISH were winners of a 2019 Making a Difference award for social responsibility.
![]() Click here for a video explaining our work on suicide prevention.
Click here for a video explaining our work on suicide prevention.
![]() Read our March 2020 update on the national suicide prevention programme in this blog, by NCISH researchers Nicola Richards and Cathryn Rodway.
Read our March 2020 update on the national suicide prevention programme in this blog, by NCISH researchers Nicola Richards and Cathryn Rodway.
![]() Read a blog on our work with NCCMH to help local areas improve suicide prevention plans, by the NCISH project manager, Dr Pauline Turnbull.
Read a blog on our work with NCCMH to help local areas improve suicide prevention plans, by the NCISH project manager, Dr Pauline Turnbull.
![]() Download a summary of how we help local areas improve suicide prevention plans.
Download a summary of how we help local areas improve suicide prevention plans.
A diverse range of multifaceted, novel projects have been established throughout this programme. See some examples of innovative work being carried out by local areas in the programme.
Collaborations and associated projects
We work collaboratively with national and international academic and health colleagues in the area of suicide prevention research. Our ongoing projects are listed below.
Clinician bereavement study: survey of the effects of patient suicide on clinicians
Mental health professionals can expect to experience the death of a patient by suicide at least once but as many as four times in their professional career. Each death can have a profound effect. In this study, conducted in collaboration with the Centre for Suicide Research at Oxford University and the Royal College of Psychiatrists, we will:
- examine the impact of patient suicide on the emotional well-being and clinical practice of clinicians
- map wanted and available resources for clinicians before and after the suicide of a patient
- make recommendations on how to develop support services locally and nationally for clinicians.
We will undertake this by using our existing NCISH methodology to identify clinicians who have experienced the death of a patient by suicide. We will invite them to complete a questionnaire focusing specifically on the impact the patient’s death had on them.
The study has been funded by the Medical Protection Society (MPS) Foundation. It will begin in April 2024 (estimated) and data collection will continue for 1 year.
Suicide in former service personnel
*NEW* findings from the first phase of the study published in PLOS Medicine.
We found the overall suicide rate was not greater than in the general population, but risk was 2-3 times higher in male and female veterans aged under 25 than in the same age groups in the general population. Male veterans aged 35 years and older were at reduced risk of suicide. Male sex, Army service, discharge under the age of 35 years, being untrained on discharge, and length of service under 10 years were associated with increased suicide risk. Factors associated with reduced risk included being married, a higher rank and deployment on combat operations.
Read our paper “Suicide after leaving the UK Armed Forces 1996-2018: a cohort study” (PLOS Medicine)
Download our key messages sheet (PDF)
Watch our Professor Nav Kapur talk about the key findings and recommendations
This study, with the Ministry of Defence, aims to investigate suicide amongst those who have left the UK Armed Forces, and to make comparisons with serving personnel and the general population. The study will update our previous work from 2009, which showed although the overall rate of suicide was not greater than that in the general population, the risk of suicide in young men who had left the Armed Forces was 2-3 times higher than in the same age groups in the general population. Since this study was carried out there has been no systematic investigation of suicide in UK veterans.
The purpose of the study is to understand the rate, timing and risk factors for suicide for those who have left the UK Armed Forces between 1996 and 2018. The study will include the linkage of data from the Ministry of Defence on all suicide deaths in serving personnel and all personnel discharged from Armed Forces with NCISH data on general population and mental health patient suicides. It will also include a review of coroner’s records and inquest hearings for a sample of veteran suicide deaths. This study will provide more detail of the factors related to suicide (particularly early and recent vulnerabilities, in-service exposures, difficulties after discharge, living circumstances, and contact with a variety of health and third sector providers) in this population.
The study is funded jointly by the Ministry of Defence and NHS England. Further information on the study design and purpose can be found in our study summary and information sheet, and is also available on the GOV.UK website.
Support for improving community-based care for self-harm
We were commissioned by NHS England and NHS Improvement to support areas in England to improve community-based services and care for people who self-harm. Together with experts from the Manchester Self-Harm Project (MaSH) and NIHR Greater Manchester Patient Safety Translational Research Centre (PSTRC), we supported participating areas by providing:
- Expert knowledge of current self-harm data and research;
- Guidance on national guidelines and recommendations for the care of people who self-harm;
- Advise on methods of data collection to monitor and evaluate the impact of service changes for people who self-harm;
- An online resource to gather useful information in an easily accessible format.
This was part of a national programme funded by NHS England and NHS Improvement linked to establishing new and integrated models of primary and community mental health care across England. Read more about this collaboration here. This work was commissioned by the Healthcare Quality Improvement Partnership (HQIP) and funded by NHS England and NHS Improvement.
Suicide Information Database Cymru (SID-Cymru) and NCISH database linkage study
National academic response to COVID-19 related suicide prevention
We extended our national suicide prevention support role to include responding to local area’s concerns specific to the pandemic. Read more about our work here.
![]() Read a blog on NCISH’s contribution to suicide prevention during COVID-19.
Read a blog on NCISH’s contribution to suicide prevention during COVID-19.
Evaluation of the Mersey Care NHS Foundation Trust Zero Suicide initiative
![]() Watch a video of Professor Louis Appleby talking about the Zero Suicide initiative
Watch a video of Professor Louis Appleby talking about the Zero Suicide initiative
Safety in marginalised groups
The impact of suicide in the UK
A survey-based study conducted in collaboration with the Support after Suicide Partnership (SASP) to better understand the impact of suicide on people’s lives, including the support received.
- Read the study’s report “From grief to hope: the collective voices of people bereaved and affected by suicide in the UK“.
All our research projects
More information on our research projects can be found within the University’s Research Explorer.