
Assessing Online
Assessment Toolkit
 The Assessment Toolkit has been designed as part of the Flexible Learning Programme, using feedback from over 150 students and staff, gathered across 12 interactive online workshops. It’s an iterative and always-evolving platform, with new information and resources being added regularly, guided by what you want to see.
The Assessment Toolkit has been designed as part of the Flexible Learning Programme, using feedback from over 150 students and staff, gathered across 12 interactive online workshops. It’s an iterative and always-evolving platform, with new information and resources being added regularly, guided by what you want to see.
Resources include: the assessment journey, assessment for flexible learners and accessible assessment – as well as information on feedback, marking and moderation. Whether you’re looking for information on how assessment works at the University, or some tips and tricks during assessment periods, the Assessment Toolkit has you covered.
Designing assessments
Elements of assessment design
Measuring what students know and can do is an essential part of teaching, and, like much of teaching, designing assessments that measure what we want them to measure is not a simple task.
“When choosing assessment items it is useful to have one eye on the immediate task of assessing student learning in a particular unit of study, and another eye on the broader aims of the programme and the qualities of the graduating student. Ideally this is something you do with your academic colleagues so there is a planned assessment strategy across a programme.” (Dunn, 2002)
Technology can enhance assessment and feedback practices by
- providing greater variety and authenticity in the design and delivery of assessments:
- improving learner engagement by offering interactive and repeatable formative assessments with integrated feedback;
- providing choice in the timing and location of assessments;
- supporting and capturing a wider range of skills e.g. simulations, e-portfolios and interactivity which are not easily assessed by other means;
- increasing opportunities for students to act on feedback;
- supporting rich, innovative approaches through the use of creative and social media;
- supporting online peer-and self-assessment activities and generating feedback;
- giving students the opportunity to choose how they store and refer to feedback;
- providing tools that provide evaluation feedback about the effectiveness of the module or course
Operationally:
- ensuring submission, marking, moderation and data storage processes are efficient and help to reduce the administrative burden;
- promoting consistency, accuracy and clarity of marking;
- speeding up assessment processes making assessment and feedback more immediate and richer;
Assessment Design Resources
- Guidance table on designing out malpractice in assessment https://documents.manchester.ac.uk/DocuInfo.aspx?DocID=55628
Assessment Rubrics
What is an Assessment Rubric?
An assessment rubric is a set of predefined criteria and scale of achievement through which students’ work can be evaluated.
As well as being an effective evaluation tool, rubrics can also be used to support and scaffold the learning process and to aid development of assessment literacy.
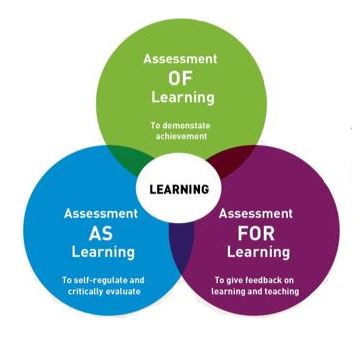
Potential Benefits:
Assessment for Learning
- can be used to provide a visual framework for students to access before writing an assignment and to provide clear guidelines on the expectations
- enables students to see what achievement of the learning outcomes involves, to seek clarification and ask questions before an assignment due date and to fully engage with this from the outset
- can be used to develop assessment and feedback literacy and to support constructive and positive conversations before the due date and afterwards around strengths and areas for improvement
Assessment as Learning
- Can be used as a tool for effective self and peer review, providing students with the language around which to discuss their own development.
Assessment of Learning
- Provides a tool for marking consistency and reliability, for both the individual marker and for inter-marker transparency
Rubrics Examples
Please find below a library of resources for reference. If for any reason you are unable to access these resources, please contact eLearning.
Alternative Methods of Submission
For information on the various methods of submission – including guidance on group and video submissions – please refer to the Managing Alternative Submissions section of this collection of guides:
https://www.staffnet.manchester.ac.uk/humanities/teaching-support/elearning/resources/turnitin/guides/#altsubmissions
You will also find and a comparison of the different submission tools: Blackboard, Turnitin and VoiceThread.
AI and assessment
Discussions around AI and assessment extend far beyond worries about AI-produced text detection and worry around malpractice. AI is integrated into many of the tools we use on a daily basis. AI and assessment is more broadly about the process of digital transformation unfolding in higher education and its practices accelerated by AI.
A number of resources are curated to support staff and students in Humanities integrate AI into their academic practice:
Support
To arrange a one to one consultation please contact the eLearning team.
Selecting methods of online assessment
Assessment methods are the means by which students demonstrate that they have met the module’s learning outcomes. There are various standard methods available to academic staff for assessing student learning in higher education.
Knowing what is possible and the respective strengths of a given method, how they should be used, is critical to effective assessment design. Assessment variety, effective student engagement with a task, and can make a significant difference to student achievement and satisfaction.
Abstract
Students are required to write an abstract of an article or on own coursework within a given word limit.
Why is useful
- Abstracts promote academic skills, self and peer assessment
- Form of assessment particularly useful in large cohorts and at PG level.
Annotated bibliography
Students produce a list of texts (primary and secondary sources, internet sites, other) on a particular topic and to a particular referencing convention. The bibliography is annotated with a commentary, which could include a critical evaluation, or why each source has been selected.
Why is useful
Annotated bibliographies tasks
- model academic and study skills
- promote concise writing
- promote critical thinking
- are difficult to plagiarise
Guidance and Tips
- Can be used as a preparation to a subsequent assignment.
- As a group task, they can be used as basis for group reading and analysis of key sources
Online Delivery
A number of tools can be used: Word document, Bb Journal, other. As a group activity Wiki tool is recommended.
Audience-specific article or report
Students are asked to write on a particular topic(s) to an agreed length in a specific style e.g. a journal, newspaper or magazine.
Why is useful
Supports development of writing skills for employability
Guidance and Tips
Submission via Turnitin is recommended to assist in plagiarism checking
Audiobooks
This mode of assessment is particularly useful in language learning and literature. Students are asked to create an audiobook and to make it available as downloadable media. In their audiobooks students may be asked to review literature in the target language and provide commentary, to develop and narrate a story.
Why is useful
- Supports development of writing skills in the target language
- Supports development of digital skills and employability
Guidance and Tips
Submission via Turnitin is recommended to assist in plagiarism checking
Further Resources
- Reaching out to (new) readers through the use of Audiobooks – Case study poster
Book review
A book review is a critical evaluation of a book (or chapter) where students is asked to describe and analyse content, form, style, quality, significance/merit or other.
Why is useful
Critical review of a book is an effective method to deepen student’s knowledge of a subject, sharpen analytical focus and critical skills, as well as teaching output-specific skills i.e. how to write and structure a Book review within a limited word count.
Guidance and Tips
- The review may involve submission to a particular journal
- Mostly used in PG teaching
Blog
Blogs are a form of online site where a student (as author) shares (with a class or beyond) in a diarised manner views or commentary on a subject matter.
Why is useful
Blogs can be used to develop
- analysis, reflective/critical thinking and peer review
- communication skills
Malpractice risk: low
Guidance and Tips
Allow Blog readers/visitors to comment on the entries
Online Delivery
Blackboard Blog Tool for restricted cohort access. If public exposure is sought there is a wide range of free blogging tools.
Further Resources
Case Study
In case study assignments students work through a complex problem, examine a situation factually, analyse different perspectives and offer critically informed recommendations or solutions.
Why is useful
- Develops analytical skill
- Encourages students’ linking theory and practice
- Authenticity, real-live value
- Malpractice risk: low
Online Delivery
Submission via Turnitin or Bb Assignment tool.
Further Resources
Vanderbuilt University Centre for Teaching, Case Studies
Concept map
Concept maps are visual representations of information, complex concepts or processes.
Why is useful
Concept maps are especially useful for students who learn better visually, although they can benefit any type of learner.
Guidance and Tips
Concept maps are useful (and potentially quick) exercises that can provide feedback to tutors on students’ understanding.
When used alongside a recommended digital tool it can enhance students digital skills.
Online Delivery
Word (Shapes) allow students to create basic concept maps. Alternatively a number of freely available tools could be used e.g. Popplet, Lucidchart.
Designing and creating a learning object
Often used in languages, students prepare a learning package on a specified or agreed topic that is addressed to fellow students or a specific audience e.g. members of the public, school children etc.
Why is useful
Predicated on the principle that learning emerges from elaboration on a topic, completion of the task (either individually or in a group) requires excellent understanding of the topic as well as pedagogic design and delivery.
Guidance and Tips
- Can be an individual or a group task
- When used alongside a recommended digital tool it can enhance students digital skills
Online Delivery
A range of free as well as supported digital applications are available to students (Adobe Spark Page, Adobe Spark Video, Xerte, other).
Diagnostic assessment
A diagnostic assessment is often a test that assist the tutor to identify levels of knowledge or skills across a cohort of students.
Why is useful
Diagnostic testing is an effective tool
- for tutors to capture diversity and levels of knowledge and understanding testing
- for student self-evaluation
Guidance and Tips
Can be used:
- at the start of a module (pre-module)
- or also effectively at the start of a class/lecture to trigger student engagement (in-class polling)
Online Delivery
Where online testing is used e.g. Blackboard Tests – automatic marking can deliver time savings as well as automated feedback to students.
For in-class setting, tools such as TurningPoint Mobile can be used for live polling as well as in off-campus remote teaching to deliver polls that students respond to in their own time (asynschronous polls).
Digital Timeline
Online digital timelines are interactive displays of text, images and media rich information that organise and convey meaning, develop narratives, or analyse complex concepts.
Why is useful
Timeline-based assignments can aid in a variety of learning goals
- Analyse non-linear relationship
- Develop historical content
- Analyse on a micro or macro scale
- Develop arguments
- Compare time periods
Guidance and Tips
Can be an individual or a group task
When used alongside a recommended digital tool it can enhance students’ digital skills
Online Delivery
Adobe Spark timeline. A range of free tools are available and you may consider giving students choice in the tools they prefer to use.
Further Resources
- Case Study: Digital Timelines – assessing the aesthetics and politics of Italian Fascism
- Vanderbilt University Centre for Teaching, Digital Timelines
Discussion
Students are assessed on the basis of their contributions to an online discussion with their peers.
Why is useful
- Student retain information longer than with other teaching methods
- Discussions are forums that can facilitate information, promote interaction and debate, promote critical thinking, problem solving, peer learning and model constructive criticism
- Perspectives from group members offer another opportunity to learn new material
- Students who establish a good relationship with their peers have a more positive learning experience
- By increasing interactivity with each other in task-oriented ways, students construct rather than acquire knowledge.
Guidance and Tips
- Discussion boards require careful design and moderation to ensure active student participation
- Discussion boards can be effective ways to handle student FAQs
Online Delivery
Online discussion can be hosted on the virtual learning environment (VLE) using either Bb Discussions tool or Piazza.
Further resources
- Gilly Salmon, Five stage model of student interaction (7 min. video)
- Drew Withworth, Gary Motteram, Online Discussions Top Tips
Dissertation
A substantial paper that is typically based on original research and that gives evidence of the candidate’s mastery both of her own subject and of scholarly method.
Why is useful
Potential for sampling a wide range of practical, analytical and interpretative skills and to assess a broad application of knowledge, understanding and skills to other situations.
Online Delivery
Submission via Turnitin
Essay
An essay is a piece of structured writing used to assess depth of knowledge, construction of arguments and synthesis of the breadth of material covered.
Why is useful
Essays test student ability to
- to produce sustained and structured academic writing
- to develop an argument in a logical way
- to comply with a range of parameters (word count, use of different sources, submission deadlines, referencing protocols)
Guidance and Tips
Malpractice risk is high if essays are factual-based.
Online Delivery
Submission via Turnitin is recommended.
Essay Plan
Instead of writing a full essay, students are asked to produce a work plan including milestones and deliverables, that demonstrates their preparation, planning and reading on a topic.
Why is useful
Encourages self-assessment, self-regulation and project management.
Guidance and Tips
- Useful for formative, self- and peer-assessment.
- Consider assigning some marks if students deliver as planned and on time.
Exam (closed book unseen)
In unseen time-constrained exams students are presented with a set of questions they have not seen and are assigned a set time in which to answer them on their own. Takes place in a controlled environment, most commonly at the end of a course unit.
Why is useful
- Widely used method of assessment.
- It can test a range of attributes e.g. knowledge and depth of understanding; analytical abilities; written communication skills; ability to synthesise information.
- Malpractice risk: very low
Guidance and Tips
- If there is a well-constructed marking scheme, candidates can be reasonably confident that the marking will be fair and consistent. Closed-book unseen exams offer low assessment validity where they measure what the candidate can write about what they have learned against the clock. Where these exams are based on e.g. problem solving, case study analysis, validity can be much higher.
- Enhancement such as students asked to apply assessment criteria to their own work can easily be incorporated.
Online Delivery
Essay-type unseen closed book exams can be delivered online via Turnitin or the Bb Test tool. However this type of short time-constrained assessment is not recommended off-campus due to the potential disadvantage to students in different time zones and difficulties in delivering online invigilation
Further resources
Race, P
Exam (closed book seen)
Students are provided with the questions to be answered, in a time-constrained context, in advance. Alternatively the examination topics may be released in advance but the precise questions are unseen until the exam
Why is useful
- Seen closed-book exams can test a range of attributes e.g. knowledge and depth of understanding, analytical abilities, written communication skills, ability to synthesise information, ability to work under a time constraint.
- Malpractice risk: increased compared to closed book unseen exams. Students may be tempted to prepare for seen exams in small groups which may result in accusations of collusion.
Guidance and Tips
Don’t set assessment questions which have only one answer or an ‘oven-ready’ answer. Choose your exam questions carefuly. Avoid words like …… ‘explain’, ‘describe’. Use instead ‘justify’, ‘create’ , ‘rank’, ‘defend’, ‘interpret’, ‘analyse’, ‘catalogue’, ‘critique’, ‘plan’, ‘invent’, ‘revise’.
Online Delivery
Essay-type seen closed book exams can be delivered online via Turnitin or the Bb Test tool. However this type of short time-constrained assessment is not recommended due to the potential disadvantage to students in different time zones and difficulties in delivering online invigilation.
Exam (open book)
Time constrained assessment task allowing students access to various reference sources during the examination e.g. textbooks, law statutes, statistics etc
Why is useful
- This method removes the over-reliance on memory and recall typical of (closed- book) exams
- Open book exams can test skills in application, analysis and evaluation.
- Models the way that professionals manage information
Guidance and Tips
- Open book exams can be seen or unseen.
- The malpractice risk is increased, compared to closed book unseen exams, but risk can be reduced by having questions which require analysis and synthesis.
- When delivered on-campus, open book exams takes place in a controlled environment and under time constraints
- When delivered online (off-campus) and over various days, exam can be a way for students to learn while doing the exam
Online Delivery
Where open book exams are delivered online off-campus, exams should be seen i.e. available to students for a period of time that sufficiently prevents disadvantage to students in different time zones while considering nature of the task and risk of malpractice. Turnitin should be used to assist in the identification of potential malpractice.
Further resources
- Sheffield Hallam Assessment Methods:Open Book Exam (pdf)
- Case study: Revising Translation assessment for online open book examinations
Exam (MCQ and short answer)
Form of assessment task where students are asked to select the best possible option out of choices from a list. MCQs tests can be used for diagnostic, formative self-assessment or summative purposes
Why is useful
Well designed questions can assess more than factual recall of information, but do take time to design. Assertion or scenario questions, True/False, or multiple response questions such as ranking or matching items can evaluate comprehension and deductive reasoning
Guidance and Tips
- Typically MCQs design require initial time investment but are time effective and efficient when assessing large numbers of students.
- Consider giving different weight to questions in accordance to their difficulty
- Malpractice risk low when used in an invigilated setting.
- To reduce the incidence of malpractice when delivered off-campus a number of test options can be used e.g. questions banks, randomised presentation of questions, disabling back-tracking, etc. Confidence-based marking (CBM) where learners must rate their confidence that their answer is correct can also be used to reduce the incidence of chance.
Online Delivery
In on-campus settings, MCQs tests can be delivered online (Blackboard Test Tool), or on paper via Optical Marking Recognition (OMR method) the later is especially useful for exams that consist of MCQ as well as essay-type questions.
In off-campus conditions, Blackboard Test of 1-2 hours as appropriate and available within a short window of 24h aim to allow for diverse time zones while minimising potential malpractice.
Further resources
Exam (Maths-based)
Testing and assessing the understanding of maths based concepts including statistics
Online Delivery
Mobius supports student learning of mathematical notation, and the delivery of continous homework assignments
Further resources
- Mario Pezzino and Elsa Lee, Adaptive testing using Mobius (Powerpoint Presentation)
Exam (oral)
In oral exams examiner poses questions and the student answers in a spoken form.
Why is useful
- Primary purpose of oral examinations is to demonstrate speaking, presentation or communication skills. They are also useful to explore students’ understanding of a wide range of topics.
- Malpractice risk: very low. Oral examination are also used mechanism in malpractice hearings to assert student knowledge.
- Can be used for assessing ‘borderline’ degree classifications
Guidance and Tips
Depending on class size they can be time consuming for staff.
Online Delivery
A web conferencing tool such as Bb Collaborate can be used to run oral examinations.
Grant Application
Activity where students develop a specific, meaningful credible and actionable plan that responds to a real or fictitious Call from a organisation, for projects or funding
Why is useful
- Engaging real-live assessment
- Develops writing and employability skills
Most relevant to PG students
Guidance and Tips
Students (individually or as a group) could be required to either
- to develop application considering overall purpose, audience, outputs as well as style and costings
- use real/adapted versions of different grant application forms to plan a research project. This could be assessed using the published criteria as a basis for the marking criteria
Provide assessment criteria to students before submission
Further resources
University of Wisconsin, Planning and Writing a Grant Proposal
Infographic
Infographics are visual representations of information that require students to distil and present key information in a visually meaningful manner or narrative.
Why is useful
- Infographics can enhance (quantitative/qualitative) analysis and critical understanding of themes
- When used alongside a recommended digital tool it can enhance students’ digital skills
Guidance and Tips
Infographics can be used for a range of purposes:
- Versus comparisons
- Data visualisation
- Making complex information visually engaging (flowchart, timelines)
Online Delivery
Adobe Spark Page.
Further Resources
Pen State University, Infographic Assignment
Journal or Reflective Diary
A journal is a regular record of news and events of a personal nature – a diary if daily – where students record experiences, accounts of critical incidents, combining narrative with a reflective commentary which could support the development of an action plan.
Why is useful
Journals, accompanied by supported Action Planning, promote pro-active learning and student metacognitive skills.
Guidance and Tips
Students working on placements keep diaries, journals or blogs in which they record their experiences. They can be asked to write about a critical incident in terms of context, what happened, the outcomes, how theoretical material they have learnt underpins the process and how they would do things differently in future.
Online Delivery
Blackboard Journal tool.
Further resources
- Case Study: Online Journals as a tool for Learning
- Case study: Reflective learning on Religion Culture and Gender
Learning Log
Account of activities, tasks, reflections or outcomes that students are asked to record to demonstrate attainment of knowledge, skills or behaviours. It can be in a diarised manner but not necessarily e.g. competence-based logs/journals.
Why is useful
- Learning logs – when accompanied by supported Action Planning – promote pro-active learning and student self-regulation
- Malpractice risk low
Guidance and Tips
Students could be asked to indicate competencies which they have practised to a specific level during a work placement.
Online Delivery
Journal tool in Blackboard
Further Resources
Media Profile
Students are asked to use pictures or headlines from newspapers and magazines, advertisement, social media etc to illustrate analyse the public perception/profile of a particular individual or theme.
Why is useful
Develops media literacy; in particular students understanding of how information is presented, meaning constructed and the significance of media.
Guidance and Tips
Useful as a group assignment.
Peer Assessment
Peer assessment is the process whereby students assess and provide feedback to fellow students about their work.
Why is useful
- Develops transferable collaborative and communication skills
- Engages students in understanding assessment criteria – supporting the development of assessment literacy
Guidance and Tips
- Let students know the rationale for doing peer review. Explain the expectations and benefits of engaging in a peer review process.
- Listen to group feedback discussions and provide guidance and input when necessary.
- Provide marking criteria (rubrics) to students and ask tudents to formulate in their own words the documented criteria before they begin the task
- encourage students to give each other feedback on an assessment in relation to the marking criteria
- Consider asking your students to add their own specific criteria to the general criteria you provided or require students in groups to generate the criteria used to assess their projects;
- Model how you would think through and solve similar tasks or providing model answer.
Varieties, such as peer scoring, involve students marking their peers’ work but without relaying feedback.
Online Delivery
Peer assessment task can be delivered through a variety of channels: online discussions (Blackboard discussion boards), written work (rubrics and Peermark), comments/feedback on Blog posts, other.
Further resources
Performance & Observation
In performance assignments students are required to give some form of performance, e.g. concert, play, dance, etc.
In observation assignments students are observed whilst undertaking some form of ‘performance’. This is commonly used in teacher education, laboratory work.
Online Delivery
In off-campus online environment web conferencing tools e.g. Blackboard Collaborate offer to closest replica to live performance and observation.
Presentation
Presentation assessments typically involve students researching, discussing and presenting on a topic for a specified length of time. Presentations often involve the production of associated slides or handout(s).
Why is useful
- Oral presentations are opportunities to develop presentational skills and on-stage confidence.
- Can usefully be combined with self- and peer-assessment
Guidance and Tips
- Can be individual or group tasks
- Student can use presentations to report research findings, introduce a new curriculum topic to their peers, reflect on experiences, other
- Share your presentation assessment criteria (rubric) with your students ahead of assessment
Online Delivery
Off campus online presentations can be delivered
- synchronously using web conferencing tools (Bb Collaborate, Zoom)
- asynchronously using VoiceThread
Multimedia presentations via VoiceThread
Further resources
Portfolio
Portfolio assessment is most suited where both process and product of student learning must be captured. In Portfolio assessment students provide evidence for their achievement of learning outcomes and these commonly incorporate a reflective commentary.
Why is useful
A portfolio encourages reflective thinking, often requiring students to collate evidence, review, select, order and annotate it and to reflect on their development.
Guidance and Tips
- Portfolio assessment is used to review a collection of artefacts or, in discursive subjects, to encourage (a) construction of meaning, (b) awareness and evaluation of own learning (c) record of student progression, e.g. academic advising.
- Portfolios can be used as tools to promote development of cross-module programme-wide knowledge and graduate programme attributes
-
Portfolios can be time-consuming to mark
-
Students may need guidance on reflective writing
Online Delivery
ePortfolios can be delivered through a variety of means: electronic submission of artefacts, reflective journals, public blogs or other.
Further resources
Poster
Students are asked to produce (and often present) a poster that synthesises and presents, in a visual manner, research or understanding of a topic.
Why is useful
Posters require the students to think distinctively, summarize and select the important factors that need to be shown.
Guidance and Tips
- Following common practice in the sciences where posters are commonly used to present at conferences, posters can be linked with presentation tasks to facilitate the development of oral presentation skills.
- posters can be a time efficient way to assess large cohorts including analytical and collaborative skills.
- Posters can be used for individually or group assessment.
Online Delivery
Production in Powerpoint and submission via Turnitin or Bb Assignment tool. Where posters are for group assessment Padlet can be the platform for both production and collaboration.
Further resources
- Case Study: Summative Group Research Posters through Padlet
Problem Sheets
Problem sheets present well-defined problems that require students to apply knowledge in order to provide a solution.
Why is useful
Problem sheets are a useful way of providing students with regular formative feedback on their work and encouraging self-assessment.
Guidance and Tips
Problem sheets can effectively be used in seminars to facilitate peer learning.
Online Delivery
Problem sheets can be delivered online via Blackboard Test or Mobius for mathematical type problems in particular.
Problem-based Task
In Problem Based Learning or Enquiry Based Learning (PBL/EBL), an initial problem serves as the trigger as well as the organising focus for student learning. The ‘teacher’ acts as a facilitator in a multi-stage process that involves problem analysis, scoping and discussion in groups, and where the student actively identifies learning issues and plan to acquire the necessary knowledge to address initial problem or to develop an approach to it.
Why is useful
Promotes elaboration of knowledge, knowledge reorganisation and serves to model self-directed learning.
Guidance and Tips
Online Delivery
Further resources
Question Bank
Ask learners, individually or in pairs, to produced MCQ tests as well as feedback for both correct and incorrect answers.
Why is useful
Students are assessed on their ability to produce a certain number of questions on a topic. This helps students to recognise what they do and do not understand about a topic and is a useful way for staff to collate a question bank that could be used for quick formative quizzes throughout the module.
Guidance and Tips
When used alongside a recommended digital tool it can enhance students’ digital skills
Online Delivery
Various tools can be used for this activity. If you like your students to create the questions but also to learn/use an digital application you can use TurningPoint Mobile or freely avialable tools like Quizlet. If you prefer to publish questions online you can select the best and put on Blackboard (Bb Test tool)
Further resources
Vanderbilt University Centre for Teaching, Classroom Assessment Techniques
Research Project
A research project assessment may involve all or some of the following aspects: students developing a research question, selecting and presenting evidence, planning their research journey, synthesing key findings and research outcomes.
Why is useful
- Potential for sampling wide range of practical, analytical and interpretative skills
- Can assess wide application of knowledge, understanding and skills.
Guidance and Tips
If linked to presentation at conferences, it can enhance student motivation and academic development
Online Delivery
Meetings with research project supervisors can easily be delivered via web conferencing tools e.g. Bb Collaborate. Submission would typically involve Turnitin.
Report, Field Report, Lab Report
Reports promote factual examination of a given situation, analysis of different perspectives and the informed recommendations.
In Field report students are required to produce a written/oral report relating to a field/site visit.
In Lab reports students are required to write a report for all (or a designated sample) of practicals in a single lab book and Lab reports.
Why is useful
Reports promote authenticity in assessment and support the development of practice skills and employability.
Role Play
Assessment where students adopt or embody a specific role in a context of real practice.
Why is useful
Supports authenticity in assessment and promotes deeper understanding of practice in specific disciplines e.g. law, teaching.
Guidance and Tips
Two possible ways to implement role play may be
- Students write or give a presentation taking on a particular role, e.g. a journal reviewer/editor, consultant, art critic etc. This type of assignment could be paired up with a grant application exercise
- Ask students to create scenarios related to a topic being discussed, which they can then share with other groups.
Online Delivery
A combination of tools can be used – synchronous or aynchronous. Video, web conferencing, discussion boards or other.
Further resources
- Learning through role play – case study
Screencast
PAGE UNDER CONSTRUCTION
Assessment where students create a screencast
Why is useful
Guidance and Tips
Online Delivery
Freely available tools like Screencast-O-Matic will allow students to create short screencasts.
Self Assessment
Self-assessment is a process of formative assessment during which students reflect on and evaluate the quality of their work and their learning, judge the degree to which they reflect explicitly stated goals or criteria, identify strengths and weaknesses in their work, and revise accordingly (Andrade & Du, 2007).
Why is useful
A record of student self-assessment and reflection provides information about the learner’s ability to evaluate their own learning.
Guidance and Tips
-
According to Boud (1995), all assessment including self-assessment comprises two main elements: making decisions about the standards of performance expected and then making judgments about the quality of the performance in relation to these standards. When self-assessment is introduced, it should ideally involve students in both of these aspects.
-
Ways to introduce self-assessment in your course may be: (a) Asking students to self-assess their own work before submission and to make a judgment about whether they have met the stated criteria and even estimate the mark they expect (b) providing online tasks where feedback and reflection on performance is integrated into the task; (c) providing self-assessment activities such as knowledge and understanding tests at the end of a lecture
Online Delivery
A number of tools will allow you to deliver self-assessment activities online e.g. TurningPoint Mobile (live as well as asynchronously) or Bb Tests (asynchronously)
Further resources
Andrade, H. & Du, Y. (2007). Student responses to criteria-referenced self-Assessment. Assessment and Evaluation in Higher Education,32 (2), 159-181
Boud, D. (1995). Enhancing learning through self-assessment. London: Kogan Page
Simulation
Assessment where students adopt or embody a specific role in a context of real practice.
Why is useful
- Useful for assessing a wide range of skills, knowledge and competencies.
- Supports authenticity and promotes deeper understanding of practice in specific disciplines e.g. law, teaching.
Guidance and Tips
Text or virtual simulations are provided for students who are then required to answer questions, resolve problems, perform tasks and take actions etc. according to changing circumstances within the simulation.
Online Delivery
Video, 3D video and virtual reality are mechanisms to assist replicating real live contexts.
Survey
Survey questionnaires present a set of questions to a subject. Designing and creating a survey questionnaire may serve research or other purposes.
Why is useful
Guidance and Tips
Online Delivery
Video (design or make)
Assessment where the choice of format is vide.
Why is useful
- Video assessment allow for the assessment of specific skills that are not easily captured by other means, such as presentation and interview skills.
- Student generated video supports development of digital and communication skills
Guidance and Tips
- Audio and video assignments can be used in place of more conventional written assignments or presentations
- Develop and share assessment criteria with your students
- Unless your assessement seeks to assess high-end video production, the need for specialist equipment is a not an issue: a number of tools are available to students (see below)
Online Delivery
Students can use a number of ways to create video
- Their own devices: mobile phone, tablet, computer, photo or video camera.
- Video presentations using VoiceThread
- Freely available tools such as Adobe Spark Video
Further resources
Web page
Assessment where building a website is one (or the main) outputs of the assessed activity.
Why is useful
The ability to put together a website is a useful real live activity and a basic digital skill in a digital world.
Guidance and Tips
Online Delivery
Adobe Spark Page (free account) will allows your students to create content and publish it to the web
Wiki
A wiki is a website where the content can be edited by anyone who has access to it. They allow students to create a variety of content in a collaborative manner
Why is useful
Wikis are a tool for collaborative group work and collaborative document writing. Wikis provide the ability to identify contributions, track progress on a group project and therefore facilitate accountability in the assessment of group work.
Guidance and Tips
Have students build a website for a fictional or real purpose.
Online Delivery
Blackboard provides a Wiki tool
Further resources
Write a Wikipedia article
A Wikipedia article or entry is a page on Wikipedia that identifies a topic, summarizes that topic comprehensively, is written in an encyclopaedic style of language, contains references to reliable sources and provides links to further resources.
Why is useful
- Getting students to write a Wikipedia entry as a form of assessed coursework can be an engaging task for students as well as a valid method to assess knowledge and understanding, analysis and synthesis, writing skills and style awareness, and expose students to group work.
- Mechanism to introduce information literacy and critical analysis of sources
Guidance and Tips
- Can be a meaningful group activity
Further resources
Wikipedia: what is an article?
